Chapter 17: Automobile Maintenance
16.1 Power system
The most widely used engines are:
- Stroke engine using gasoline as fuel
- Combustion engine using diesel
Idle: Its function is to prevent the engine from stalling when not in gear. A high idle increases fuel consumption.
Air filter: Dirt in the filter increases fuel consumption (check more often in summer).
Accelerator: Determines the amount of fuel, the more you accelerate the greater the consumption.
16.2 Electrical system
Lighting: Adjust the headlights, if poorly adjusted:
- If they are too high: it can cause glare for other vehicles.
- If they are too low: you will not see the road sufficiently.
Ignition: Spark plugs.
Charging circuit: Provides energy and recharges the battery.
When the engine is running, the energy that is spent is from the alternator and when the vehicle is stationary, it is consumed directly from the battery.
A battery does not generate power, it only collects it. For maintenance:
- Keep the terminals covered with grease or Vaseline.
- Add only distilled water, never sulfuric acid. For maintenance free batteries, you will never have to add anything
- If the engine will not start, it could be because the battery is empty or has exceeded its useful life
16.3 Lubrication system (oil)
Check the oil level cold in a horizontal position using the dip stick.
Change the oil hot, new oil is added through the fill hole when indicated by the manufacturer.
Check the oil indicator on the dashboard. If lit, this indicates a lack of oil.

16.4 Cooling system (water)
Water is cooled in the radiator by a fan. Periodically you need to check the liquid level. When adding new coolant water, you will have to take into account the degree of freezing of the liquid.
16.5 Steering system
Allows the driver to direct the movement of the vehicle to follow the desired path.
At low speed, the progressive power steering minimizes the effort required to move the steering wheel.
16.6 Suspension system
Responsible for maintaining the stability of the vehicle.
If the suspension is in poor condition, the rear of the vehicle will rise excessively when braking. It can also cause an oscillation of lights which can blind other drivers.
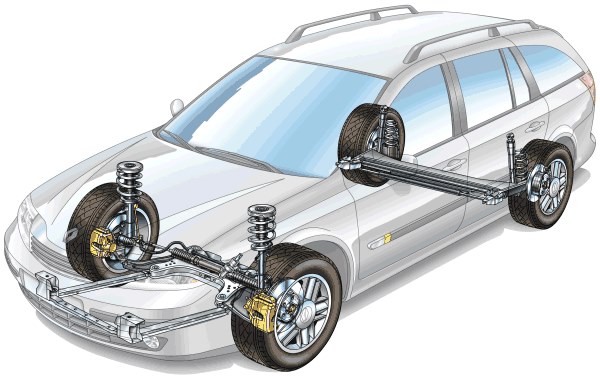
16.7 Transmission system
Automobiles are moved by the force of an engine, which is transmitted to the drive wheels.
The gearbox, whose function is to select the right gear at all times. If you notice that it’s difficult to change gears, it is most likely because of a lack of oil.
The clutch allows the movement of the engine to reach the wheels, if on accelerating the movement does not reach the wheels, it is because it is engaged.
Vehicles may be:
- Front wheel drive: the front wheels are the drive wheels.
- Rear wheel drive: the rear wheels are the drive wheels.
- Four-wheel drive: all wheels are drive wheels (4x4).
Check the steering wheel when it becomes too stiff or too loose.
16.8 Maintenance
Keeping your vehicle well-maintained, especially tyres, and passing technical inspections (ITV), when necessary, prevents many accidents.
Required spare parts for passenger cars are:
- a spare tire or temporary use tyre (with the necessary tools to change it)
- 2 warning triangles
- reflective vest (2 are recommended)
Fumes:
- White: normal
- Bluish: burning oil.
- Black: poor engine tuning, dirty air filter, excess fuel in the mixture.




