Chapter 12: Visibility and Road Hazards
12.1 Visibility
Demister device: a device that de-fogs the glass through hot jets of air.
Anti-frost device: filaments in the glass that heat slightly and de-fog the glass or prevents ice from forming.
Mirrors
Mandatory mirrors are the exterior Left-hand side and rear-view inside mirrors. If this requirement is not met (e.g. if blinds or tinted glass are used and you cannot see in the interior mirror), the outside LEFT and RIGHT exterior mirrors are mandatory.
A rear-view interior panoramic mirror does not replace any mandatory mirror.
To adjust the mirror, the vehicle must be immobilized on a flat, horizontal place. Even if mirrors are properly adjusted, there is always an area that you cannot see because of the body, called the blind spot.
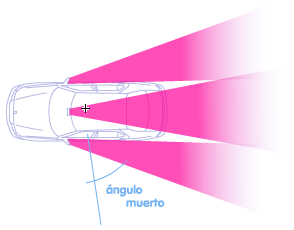
You should look in the mirrors briefly several times.
- Every 5-10 seconds on urban roads or inter-urban roads with heavy traffic
- Every 10-15 seconds on inter-urban roads in general
 The exterior mirrors are convex and the vehicle behind you appears smaller and further away. To be well-adjusted, you should be able to see a bit of the back of the vehicle, NOT the side.
The exterior mirrors are convex and the vehicle behind you appears smaller and further away. To be well-adjusted, you should be able to see a bit of the back of the vehicle, NOT the side.
The rear-view interior mirror is flat and for it to be well adjusted, you must be able to see 3 or 4 sides of the rear window.
Windscreen wipers
Always use the slowest possible speed.
12.2 Hazards on the road
Night driving:
- Adapt speed to the area illuminated by the lights of your vehicle.
- Avoid glare (slow speed, even coming to a stop).
- Use regulated and clean headlights.
Bends:
- Avoid veering out of the bend (centrifugal force), causes: High speed, heavy load, tight bends.
- Before entering: Slow down. While in the bend: Accelerate smoothly.
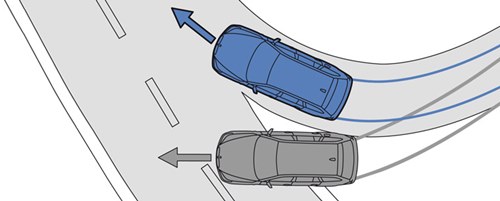
An example of centrifugal force would be clothes spinning in a washing machine, which stick to the outside because of the force of the rotation.
Rain:
- Reduce speed
- + Front distance and braking distance (double)
- - Traction and visibility. Use appropriate lighting
- Hazards: hydroplaning, check brakes, don’t splash, fogging windows
- You should be most cautious when the rain first starts
Snow:
- Reduce speed
- + Front distance and braking distance
- - Traction and visibility
- Use chains or other approved devices. Chains are used at least on the drive wheels, recommended to use high gear and have a full tank.
- It is advisable to drive in the tracks from other vehicles, as this will increase adhesion.
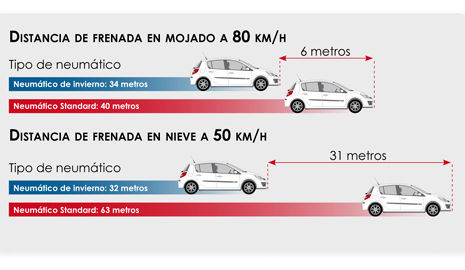
BREAKING DISTANCE IN THE WET AT 80KPH
- WINTER TYRE: 34m
- STANDARD TYRE: 40m
BREAKING DISTANCE IN SNOW AT 50KPH
- WINTER TYRE: 32m
- STANDARD TYRE: 63m
Fog:
- Reduce speed
- + Front distance and braking distance
- - Traction and visibility
- Use proper lighting (do not use high beams)
- Hazards: chain collisions, recommended to guide yourself by road markings
Ice:
- Reduce speed
- + Front distance and braking distance (by 10 times)
- - Traction and visibility
- Hazards: use chains or other approved devices. Chains are used at least on the drive wheels, use caution at dawn and at night. In case of snow, you can use tires with studs or M&S
Heat:
- + Reaction time
- + Fatigue (recommendable to take more breaks)
- + Aggressiveness
- Sun: Wear sunglasses, clean the windows
Smoke: Same as fog.
Wind (Cross winds): More dangerous from the side (lateral winds) and with gusts of wind. Dangerous to overtake a large vehicle, or at the intersection with another vehicle. Motorcycles and mopeds are the most affected by lateral winds.




